Have you ever found yourself watching a gripping movie scene or playing an intense video game, only to be pulled out of the experience by a frustrating delay between what you see and what you hear? This annoying lag, known as audio latency, can turn an immersive moment into a jarring one. As an audio technician with over a decade of experience, I’ve seen countless speakers, and I can tell you that understanding and testing for latency is crucial, especially before you commit to a purchase. This guide will arm you with practical, real-world methods to assess speaker latency, ensuring your next audio investment delivers a perfectly synchronized sound experience.
Understanding Speaker Latency: What It Is and Why It Matters
Audio latency refers to the time delay it takes for an audio signal to travel from its source (like your phone or computer) to your ears through a speaker. This tiny gap, measured in milliseconds (ms), can significantly impact your listening experience, depending on your activity.
For casual music listening, a slight delay might go unnoticed. However, for dynamic applications like video gaming, watching movies, or engaging in video calls, latency becomes a critical factor. Imagine trying to play a rhythm game where the sound is consistently off-beat, or watching a character speak with their lips moving noticeably before their voice reaches you – it quickly becomes disruptive and diminishes enjoyment. High latency can lead to a disconnect, making your audio setup feel sluggish and unresponsive.
 A frustrated gamer experiencing audio lag with their wireless headphones while playing.
A frustrated gamer experiencing audio lag with their wireless headphones while playing.
Generally, an audio latency under 150 milliseconds is considered acceptable for most casual listening and video viewing. However, for serious gamers or those who demand perfect synchronization, aiming for a delay under 80 milliseconds is ideal. Wired connections typically offer the lowest latency, often around 5-20ms, while wireless options like Bluetooth can vary significantly.
Latency Considerations Across Different Speaker Types
The type of speaker you choose can influence its inherent latency and how much it matters for your intended use.
Portable Bluetooth Speakers
These speakers prioritize convenience and mobility. They’re fantastic for on-the-go music, picnics, or casual gatherings. For these uses, a slight delay is often negligible. However, if you plan to use a portable Bluetooth speaker for watching videos on a tablet or phone, pay attention to potential lip-sync issues. Newer models with advanced Bluetooth codecs tend to perform better.
Desktop Bluetooth Speakers
Often used with computers for gaming, video calls, or daily entertainment, desktop speakers might demand lower latency. Many desktop speakers offer both Bluetooth and wired (AUX or USB) connection options, allowing you to choose the lowest latency path when critical. Their design often allows for better integration of advanced audio processing, which, while beneficial for sound quality, can sometimes subtly contribute to latency if not optimized.
Waterproof and Outdoor Speakers
Built for durability in challenging environments like poolsides or outdoor adventures, these speakers prioritize ruggedness over ultra-low latency. Given their typical usage scenarios, where precise audio-visual synchronization is rarely a primary concern, a higher latency profile is usually acceptable.
Practical Methods to Test Speaker Latency Before You Buy
You don’t need a professional lab to get a good sense of a speaker’s latency. Here are some effective, practical methods you can use:
Subjective Latency Tests: Using Your Ears and Eyes
These methods rely on your personal perception and are excellent for real-world scenarios.
The Video Synchronization Test
This is one of the easiest and most effective ways to spot latency.
- How to Perform: Use a video with clear, repetitive audio-visual cues. YouTube offers many “audio sync test” videos featuring bouncing balls, clapperboards, or simple lip-sync tests. Play one of these videos on your device and connect it to the speaker you’re testing.
- What to Look For: Observe any discrepancy between the visual event (e.g., the ball hitting the ground, the clapperboard snapping shut, or someone’s lips moving) and the corresponding sound. A noticeable delay indicates higher latency.
The Metronome/Beat Tapping Test
This test provides a slightly more quantitative subjective measurement of your perceived delay.
- How to Perform: Search online for “audio latency tester” or “metronome tap test.” These web-based tools often play a regular beat, and you’re asked to tap a button precisely when you hear the sound. The tool then calculates the average delay between the audio playback and your tap.
- What it Measures: While it includes your reaction time, consistent readings across different speakers can help you compare their relative latency and determine which feels more responsive to you.
Objective Latency Tests for Mobile Devices (App-Based)
For a more objective measurement, especially if you’re evaluating a speaker’s performance with an Android device, certain apps can provide concrete data.
Using OboeTester (for Android)
OboeTester is a utility designed for Android developers, but it can be a useful tool for consumers to get a technical reading.
- What it Is: An application available on the Google Play Store that measures “round-trip audio latency.” This means it measures the total delay from when a sound is generated, played through the speaker, picked up by the device’s microphone, and processed back.
- How it Works (Simplified): The app generates a precise audio tone, plays it through the device’s speaker (which would be your connected Bluetooth speaker in this test), and simultaneously records the sound through the device’s built-in microphone. By analyzing the time difference between the output and input, it calculates the latency.
- Availability: You can download OboeTester directly from the Google Play Store. Simply launch the app, select the “ROUND TRIP LATENCY” option, and tap “MEASURE” to get a millisecond reading.
Key Factors Influencing Speaker Latency
Understanding what causes latency can help you choose a speaker wisely.
Connection Type: Wired vs. Wireless
- Wired Connections (AUX, USB): These are the champions of low latency. A physical cable provides a direct, uninterrupted path for the audio signal, minimizing processing and transmission delays. For critical listening or competitive gaming, wired is always the preferred choice.
- Wireless Connections (Bluetooth, Wi-Fi): While offering unparalleled convenience, wireless technologies inherently introduce some delay. The audio signal must be encoded, transmitted wirelessly, and then decoded by the speaker. Each of these steps adds a tiny bit of time.
Bluetooth Audio Codecs
Bluetooth isn’t a single standard; it uses different audio codecs to transmit sound. The codec employed by both your source device and your speaker plays a significant role in latency.
- SBC (Subband Codec): The universal default. It offers decent sound but generally has the highest latency.
- AAC (Advanced Audio Coding): Commonly used by Apple devices, it provides better sound quality than SBC with moderate latency.
- aptX (especially aptX Low Latency): Qualcomm’s aptX codecs are designed for improved audio quality and, critically, lower latency. aptX Low Latency (aptX LL) is specifically engineered to reduce delay to near-imperceptible levels (often below 40ms), making it ideal for video and gaming.
- LDAC: Sony’s high-resolution audio codec offers superior sound quality but its latency can vary depending on the chosen quality setting, sometimes being higher than aptX LL.
- “Gaming Modes”: Many modern Bluetooth headphones and some speakers now feature a dedicated “gaming mode” that prioritizes low latency by switching to a faster, albeit sometimes lower-fidelity, codec.
Internal Speaker Processing
Modern speakers often incorporate Digital Signal Processing (DSP) to enhance sound quality, provide equalization, or create specific soundstage effects. While these features can dramatically improve audio, they require processing time, which can introduce slight additional delays. High-quality speakers are designed to minimize this impact, but it’s a factor to be aware of.
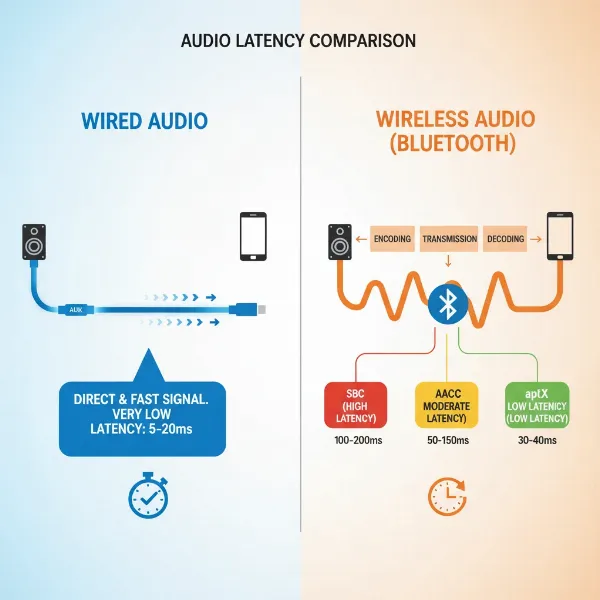 Infographic comparing wired vs. wireless audio connection latency with different codecs.
Infographic comparing wired vs. wireless audio connection latency with different codecs.
What’s an Acceptable Latency? Your Buying Guide for Different Uses
The “ideal” latency depends heavily on how you intend to use your speaker.
- For Music Listening (Casual): If your primary use is streaming music where visual synchronization isn’t a factor, latency up to 150-200ms is often perfectly fine and won’t detract from your enjoyment. Focus on sound quality and battery life here.
- For Video and Movies: To avoid noticeable lip-sync issues, aim for speakers with latency under 100-150ms. Speakers supporting AAC (especially for Apple users) or aptX codecs are good choices.
- For Gaming (Competitive): This is where latency is most critical. For serious gaming, you want the lowest possible delay, ideally under 50-80ms. A wired connection is usually superior. If going wireless, look for speakers or headphones with aptX Low Latency or a dedicated gaming mode.
- For Live Audio and Music Production: Absolute minimal latency is non-negotiable. For these professional applications, wired connections with specialized audio interfaces are essential, often aiming for sub-10ms latency. Consumer-grade Bluetooth speakers are generally unsuitable for this purpose.
At lower price points, you’ll typically find speakers relying on standard SBC codecs, which might have higher latency. As you move into mid-range options, you’ll start seeing support for codecs like AAC and aptX, offering a better balance of audio quality and reduced latency. Premium speakers often feature the most advanced low-latency codecs, robust DSPs optimized for minimal delay, and sometimes even proprietary technologies to ensure the fastest possible audio delivery. Consider your budget in relation to your most demanding use case.
Top Tips for Minimizing Latency
Whether you’re testing before buying or trying to optimize your current setup, these tips can help.
- Prioritize Wired Connections: When the lowest latency is paramount (e.g., gaming, watching synced video), always opt for a wired connection (AUX, USB) if available.
- Look for Low-Latency Codecs: Specifically search for speakers and headphones that support aptX Low Latency (aptX LL). Remember that both your source device (phone, computer) and your speaker must support the same codec for it to function.
- Utilize “Gaming Modes”: If a speaker or headset advertises a “gaming mode,” activate it. These modes are designed to prioritize speed over maximum audio fidelity.
- Keep Firmware Updated: Manufacturers often release firmware updates that can improve Bluetooth performance and potentially reduce latency. Check for updates for both your speaker and your source device.
- Reduce Interference: For Bluetooth connections, keep your source device close to the speaker and avoid obstructions. Strong Wi-Fi signals or other Bluetooth devices can sometimes cause interference that subtly increases delay.
- Connect Devices Directly: When possible, connect your audio source directly to the speaker instead of routing it through multiple devices or hubs, which can add processing steps and latency.
| Feature/Scenario | Wired Connection | Bluetooth (SBC) | Bluetooth (aptX LL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Typical Latency (ms) | 5-20 | 150-300 | 40-80 |
| Best for Gaming | Yes | No | Yes (with compatible devices) |
| Best for Movies | Yes | Acceptable (may notice sync issues) | Yes |
| Portability | Low | High | High |
“Understanding latency is key to a truly immersive audio experience, especially as we rely more on wireless technology. A few milliseconds can make all the difference.” – Admin, bluetoothspeakerusa.com
Conclusion
Choosing the perfect Bluetooth Speaker goes beyond just sound quality and battery life; understanding and testing for audio latency is a critical step to ensure your listening experience is seamless and enjoyable. By using simple visual-audio tests, tapping rhythmically, or even utilizing mobile apps like OboeTester, you can effectively gauge a speaker’s performance before making a purchase. Remember to consider your primary use case—whether it’s casual music, movie nights, or intense gaming—and prioritize speakers that offer the right balance of connectivity, codecs, and processing power for your needs. Don’t let frustrating delays diminish your audio pleasure.
What’s your go-to method for testing speaker latency, and how much does it impact your speaker buying decisions?
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a good latency for Bluetooth speakers?
Generally, a latency under 150 milliseconds is considered acceptable for most casual listening and video viewing. For critical applications like gaming, aiming for under 80 milliseconds is ideal, often requiring specific low-latency codecs or wired connections.
Can I reduce latency on my current Bluetooth speaker?
Reducing latency on an existing speaker is limited by its hardware and supported codecs. Ensure your device supports a low-latency Bluetooth codec (like aptX Low Latency) if your speaker does. Keeping firmware updated and minimizing interference can also help slightly.
Why do some speakers have more latency than others?
Latency varies due to several factors, including the type of connection (wired vs. wireless), the Bluetooth codec being used, the speaker’s internal processing capabilities, and even the source device transmitting the audio. Advanced codecs and dedicated hardware can significantly lower delay.
Does speaker placement affect latency?
For practical consumer use, the physical distance between you and the speaker does not significantly impact electronic latency, although sound physically takes time to travel through the air (roughly 3ms per meter). This acoustic delay is usually negligible for typical listening distances compared to electronic latency.
Is wired always better for low latency?
Yes, wired connections almost always offer the lowest latency because they bypass the encoding, transmission, and decoding processes inherent in wireless technologies like Bluetooth. This makes them the preferred choice for applications where minimal delay is critical, such as competitive gaming or music production.
